Настройка переброса портов в Windows
В ОС Windows, начиная с Windows XP, существует встроенная возможность установки перенаправления сетевых портов (). Благодаря этой возможности входящее TCP соединение на любой порт) можно перенаправить на другой порт или даже на другой компьютер. Причем не обязательно, чтобы в системе был сервис, слушающий данный порт.
Функционал настройки порт-форвардинга в Windows реализуется через режим команды Netsh. Синтаксис команды следующий:
- – локальный адрес, на котором будет ожидаться соединение (Внешний IP адрес)
- – локальный порт, который должен слушаться (на него ожидается соединение). Внешний порт.
- – TPC порт, на который перенаправляется соединение с порта listenport (Внутренний порт)
Допустим наша задача, заставить службу RDP отвечать на нестандартном порту, например, 3340 (этот порт, конечно, можно в настройках самой службы, но мы используем именно RDP для упрощения демонстрации техники перенаправления).
командную строку с правами администратора
netsh interface portproxy add v4tov4 listenport=3340 listenaddress=10.10.1.110 connectport=3389 connectaddress=10.10.1.110

С помощью netstat проверим, что на компьютере стал прослушиваться порт 3340:

Определить процесс, который слушает этот порт можно с помощью его PID (в нашем примере PID – 336):
Попытаемся подключиться к этому компьютеру с удаленной системы с помощью любого rdp клиента. В качестве rdp-порта нужно указать 3340 (порт указывается после двоеточия после адреса rdp-сервера):
Подключение должно успешно установиться.
. Проверьте, что в настройках вашего файервола (брандмауэра Windows или стороннего сетевого экрана, такие часто включаются в состав антивирусного ПО) разрешены входящие подключения на новый порт. В случае необходимости в брандмауэр Windows можно добавить новое правило командой:
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=”RDP_3340” protocol=TCP dir=in localip=10.10.1.110 localport=3340 action=allow
Выведем на экран список всех правил перенаправления в системе:
netsh interface portproxy show all
В нашем случае присутствует только одно правило форвардинга с порта 3340 на 3389:
Listen on ipv4: Connect to ipv4:
Address Port Address Port
————— ———- ————— ———-
10.10.1.110 3340 10.10.1.110 3389
interface portproxy dump
#========================
# Port Proxy configuration
#========================
pushd interface portproxy
reset
add v4tov4 listenport=3340 connectaddress=10.10.1.110 connectport=3389
popd
# End of Port Proxy configuration

Чтобы удалить определенное правило перенаправления:
netsh interface portproxy delete v4tov4 listenport=3340 listenaddress=10.10.1.110

Чтобы очистить все имеющиеся правила перенаправления:
netsh interface portproxy reset
Такая схема перенаправления работает только для TCP портов, UDP порты перенаправить не удастся. Также нельзя использовать в качестве connectaddress адрес 127.0.0.1.
Если нужно перенаправить входящее TCP соединение на другой компьютер, команда может выглядеть так:
netsh interface portproxy add v4tov4 listenport=3389 listenaddress=0.0.0.0 connectport=3389 connectaddress=192.168.1.100
Еще одной неявной фитчей portproxy является возможность создать видимость локальной работы любого удаленного сетевого сервиса.
Например, создадим такое перенаправление с локального порта 8888 на удаленный адрес 213.180.204.3:
netsh interface portproxy add v4tov4 listenport=8888 connectport=80 connectaddress= 213.180.204.3 protocol=tcp
Теперь, если в браузере перейди по адресу , откроется стартовая страница Yandex. Т.е. несмотря на то, что браузер обращается к локальному компьютеру, в нем открывается удаленная страница.
Перенаправление портов также можно использовать, чтобы пробросить порт с внешнего адреса сетевой карты на порт виртуальной машины, запущенной на этом же компьютере.
=bridge – Change to the ‘
netsh bridge dump – Display a configuration script.
netsh bridge install – Install the component corresponding to the current context.
netsh bridge set – Set configuration information.
netsh bridge show – Display information.
netsh bridge uninstall – Remove the component corresponding to the current context.
=bye – Exits the program.
=commit – Commits changes made while in offline mode.
=delete – Delete a configuration entry from a list of entries.
netsh delete helper Remove the specified helper DLL from netsh.
Note that after a helper is removed, it is no longer supported by netsh.
=dhcpclient – Change to the ‘
netsh dhcpclient list – List all the commands available.
netsh dhcpclient trace enable – Enable tracing for DHCP client and DHCP QEC.
netsh dhcpclient trace disable – Disable tracing for DHCP client and DHCP QEC.
=dnsclient – Changes to the `netsh dnsclient’
‘netsh interface 6to4’
‘netsh interface ipv4’
‘netsh interface ipv6’
‘netsh interface isatap’
‘netsh interface portproxy’
‘netsh interface tcp’
‘netsh interface teredo’
=lan – Change to the ‘
netsh lan add – Add a configuration entry to a table.
netsh lan delete – Delete a configuration entry from a table.
netsh lan dump – Display a configuration script.
netsh lan export – Save LAN profiles to XML files.
netsh lan reconnect – Reconnect on an interface.
netsh lan set – Configure settings on interfaces.
netsh lan show – Display information.
=namespace – Change to the `netsh namespace’
‘netsh ras aaaa’
‘netsh ras diagnostics’
‘netsh ras ip’
‘netsh ras ipv6’
‘netsh rpc filter’
=unalias – Delete an alias.
=wfp – Change to the `netsh wfp’
- Netsh commands: starting the command prompt
- How Netsh works
- Netsh commands and their contexts
- Syntax parameters for Netsh – what do they mean?
Netsh commands: starting the command prompt
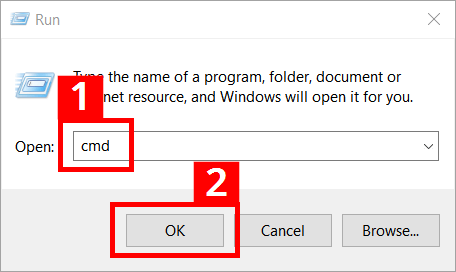
- Press the key combination [Windows] + [R]
- Enter “cmd” in the entry field (1)
- Click the “OK” button (2)
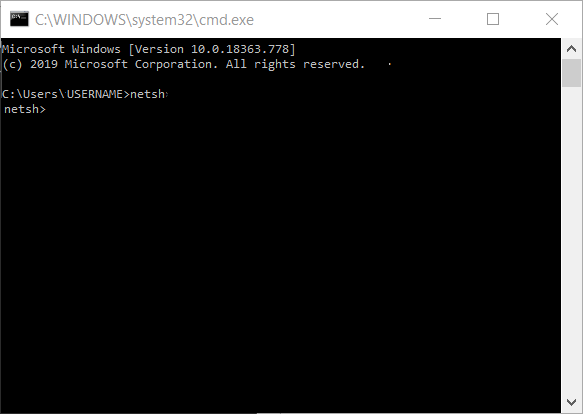
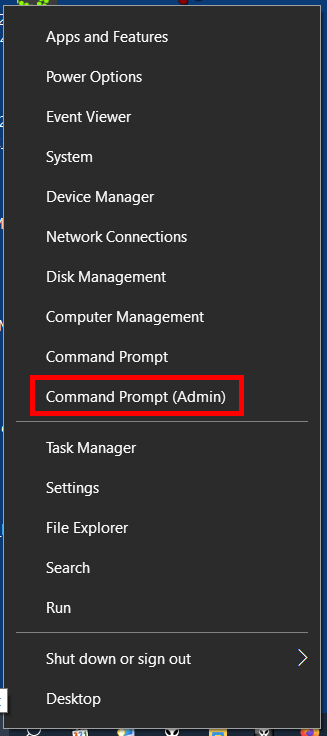
- Right-click on the Windows symbol on the left side of the task bar or press the key combination [Windows] + [X].
- Choose the entry “Command Prompt (Admin)” in the context menu that appears:
Launching the file is even faster by using a shortcut. Once created, a simple mouse click will be enough to launch the command entry:
- Right-click on the Windows desktop. Click on the menu entry “New” (1) and then click on “Shortcut” in the next context menu (2):
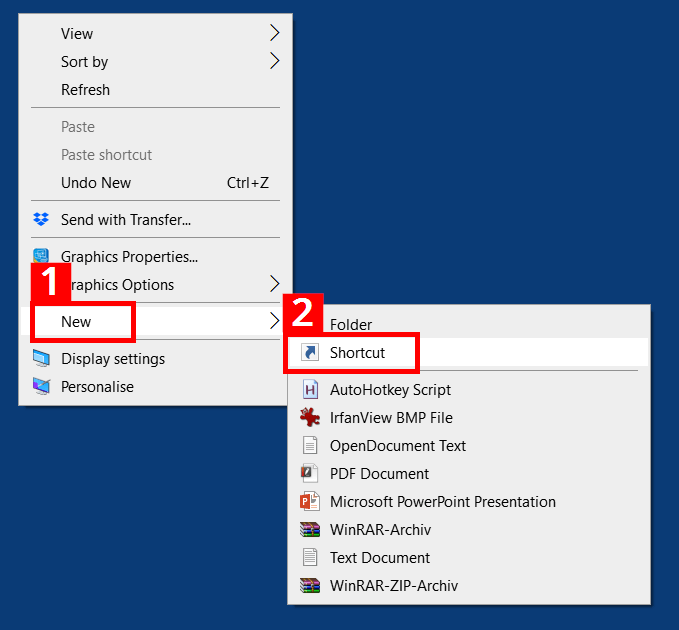
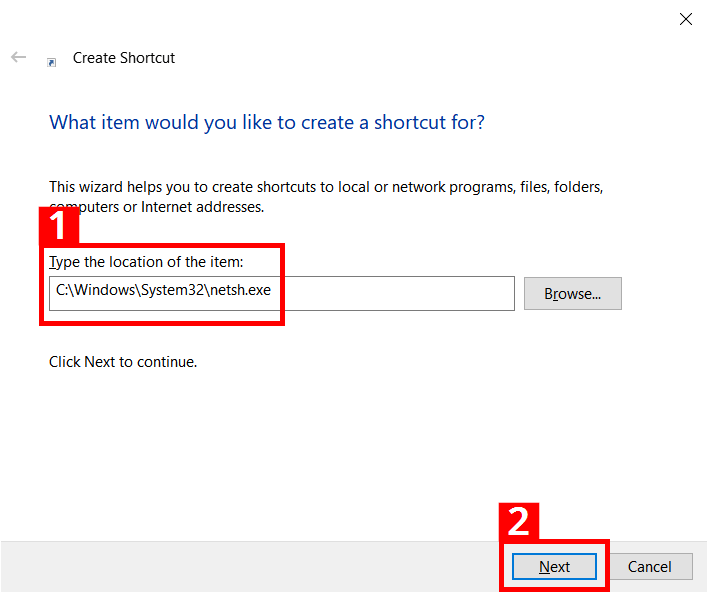
- In the shortcut assistant, enter the path C:\Windows\System32\netsh.exe (1) and click on “Next” (2):
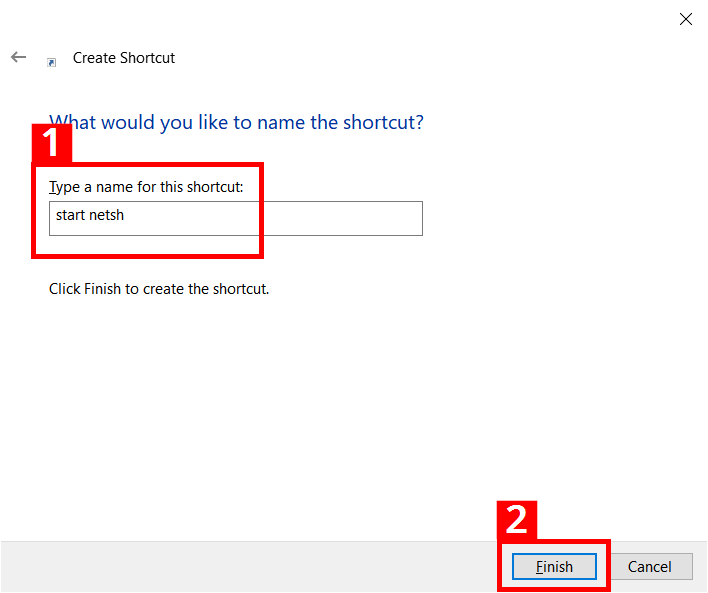
- You should give the shortcut a suitable name (1); the shortcut will then be placed on the desktop after clicking “Finish” (2):
How Netsh works
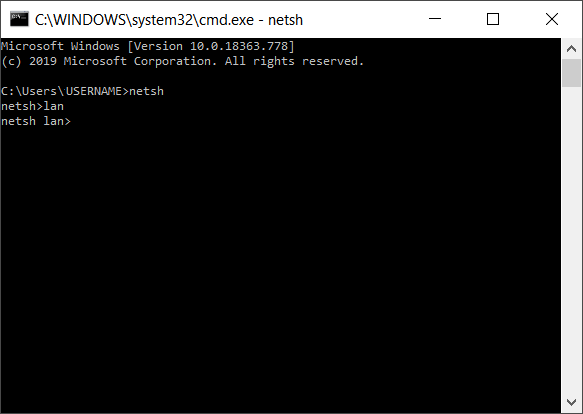
- After opening the command prompt, enter “netsh” and confirm with [Enter].
- Then enter “lan” and confirm with [Enter].
- The command prompt will now show the context change: netsh lan>
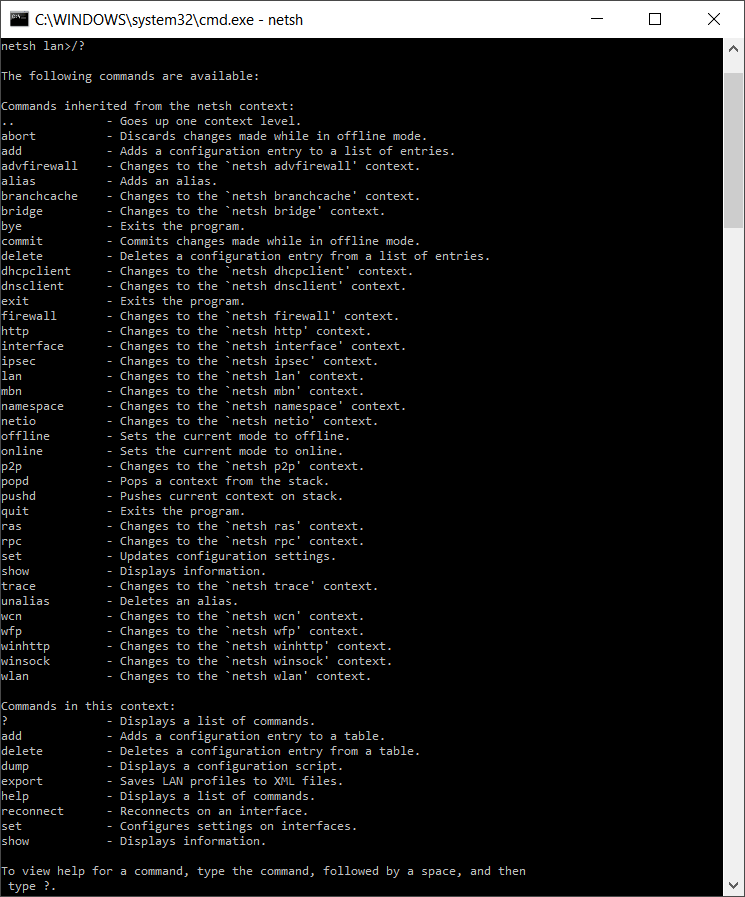
For instance, if you switch to the firewall context, the associated command reference will look like this:
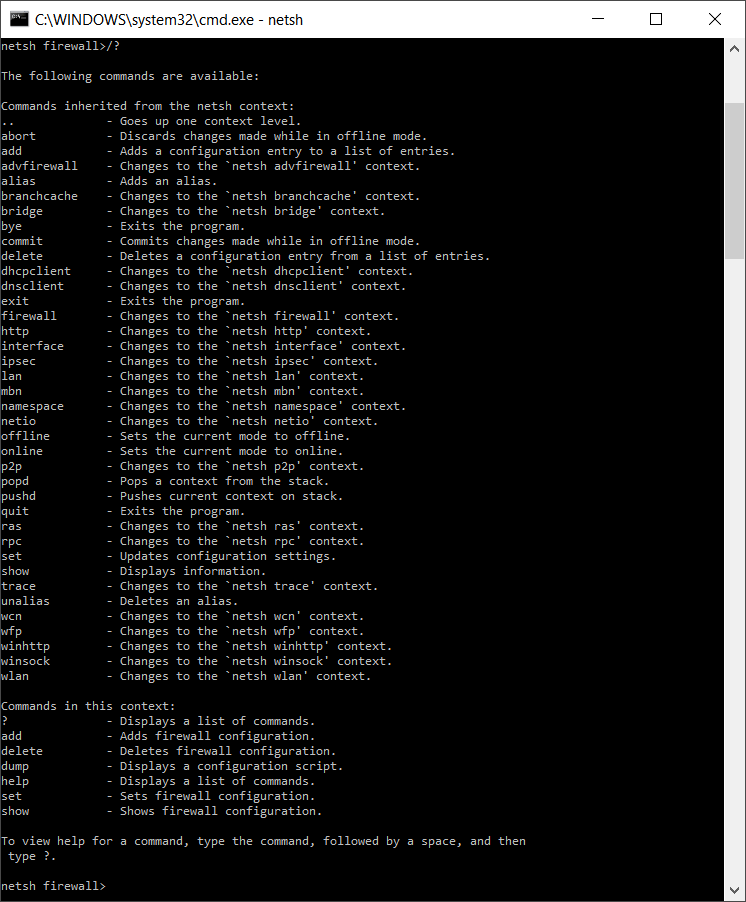
Besides the context-bound structure, there are other special points to consider when using the program. Netsh can either be used in a non-interactive or interactive mode. In the non-interactive mode, for example, important network settings are exported to a text file and reimported for subsequent recovery.
In the interactive mode, direct requests can be initiated. If you enter “netsh interface ip show address”, the current IP address of the computer will be displayed. The interactive mode can be used online or offline. The online model directly implements operations, while the offline mode saves actions and runs them later. The saved actions are activated at the desired time via the Netsh command “commit”.
Netsh commands and their contexts
Syntax parameters for Netsh – what do they mean?
netsh [-a AliasFile] [-c Context] [-r RemoteComputer] [-u [DomainName\]UserName] [-p Password | *] [command | -f ScriptFile]Resetting the TCP/IP Stack with Netsh
A protocol file can also be created that logs the changes made:
netsh int ip reset c:\tcpipreset.txtAfter running the reset, the computer will need to be restarted.
Netsh commands can also be used in batch files (*.bat) to automate routine tasks. Find out more in our guide “Removing Batch Files”.
Importing and exporting network settings
Netsh allows you to export current network settings into a plain text file. In case of network problems, a functioning and error-free configuration can then be quickly restored.
In the first step (export), the network configuration is read out, written into a text file (netcnfig.txt)), and saved in the example directory “Network Configuration” on the C:\ drive. Before the first export, you’ll need to manually create the “Network Configuration” folder on the destination drive (Netsh does not perform this step automatically). Then, switch to the command prompt and enter the code below:
netsh -c interface dump>c:\Network Configuration\netcnfig.txtnetsh -f c:\Network Configuration\netcnfig.txtWindows 10 also supports copy and paste in the command prompt. You can simply copy the command syntax from this article and insert it into the entry window.
IP configuration with Netsh
A prevalent use case for Netsh is changing IP settings. If a computer in the network doesn’t contain a static IP address but an automatically assigned one, the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is used. This communication protocol automatically assigns IP addresses to clients in a network, and other required configuration data. This process takes multiple steps:
In the first step, the current settings and names of the available network adapters are requested:
netsh interface ipv4 show interface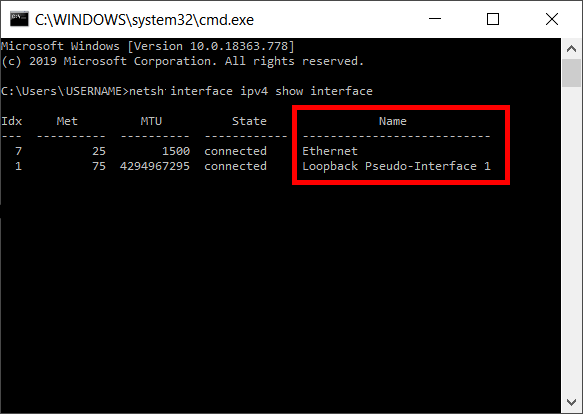
Now a certain LAN adapter (in this case: Ethernet) is determined as the addressee for the IP assignment via DHCP.
netsh interface ipv4 set address name="Ethernet" source=dhcpActivating and deactivating Windows firewall
netsh firewall set opmode enable netsh firewall set opmode disableRelated articles
What is Netcat?
Netcat is a true all-rounder in networks. Fault diagnostics, chats, extensive data transfers, and network security all form part of the impressive repertoire offered by the command line tool. But if it ends up in the wrong hands, it can also be misused. IT managers should therefore familiarize themselves with the tool.
What is Netcat?

Introduction to netstat: what is netstat and how does it work?
Introduction to netstat: what is netstat and how does it work?

Port tests: Checking open ports with a port check
Port tests: Checking open ports with a port check
How to use Netsh?
To run a netsh command, you must start netsh from the Cmd.exe prompt and change to the context that contains the command you want to use.
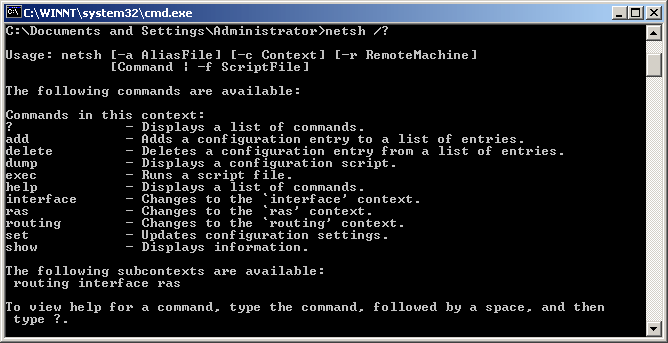
Netsh.exe is available on Windows 2000, Windows XP and Windows Server 2003.
netsh
Syntax
netsh [-a AliasFile]
[-c Context]
[-r RemoteMachine]
[Command | -f ScriptFile]-a AliasFile Specifies that an alias file is used. An alias file contains both a list of netsh commands and an aliased version of each. You can use the aliased command to shorten a Netsh command.
-c Context Specifies the default context for subsequent commands at the Netsh command prompt. Without the -c option, the default context is the root context netsh>.
-r RemoteMachine Specifies that the Netsh commands are run against a remote computer, as specified by either its computer name or IP address.
Command Specifies the netsh command to run. You must specify a full Netsh command, complete with parameters. Otherwise, Netsh displays command-line help. If the -c option is used, the context is included as part of the Netsh command.
-f ScriptFile Specifies that all of the Netsh commands in the ScriptFile file are run.
Available commands after you have entered the netsh command (typing netsh at the prompt and pressing enter).
Discards changes made while in offline mode.
.. Goes up one context level. ? Displays a list of commands. abort add Adds a configuration entry to a list of entries. alias Adds an alias. bye Exits the program. commit Commits changes made while in offline mode. delete Deletes a configuration entry from a list of entries. dump Displays a configuration script. exec Runs a script file. exit Exits the program. help Displays a list of commands. interface Changes to the `interface’ context. offline Sets the current mode to offline. online Sets the current mode to online. popd Pops a context from the stack. pushd Pushes current context on stack. quit Exits the program. ras Changes to the ‘ras’ context. routing Changes to the ‘routing’ context. set Updates configuration settings. show Displays information. unalias Deletes an alias.
Related links
Similar articles
Для чего нужны сетевые адаптеры?
Прежде чем объяснять, как их удалить, давайте поговорим о том, как сетевые адаптеры работают . По сути, мы можем сказать, что это физическое устройство, которое мы подключили к компьютеру, и что оно позволит нам установить сетевое соединение.
Эти устройства могут быть как внутренние, так и внешние . Сетевая карта может быть интегрирована в материнская плата сам, но также то, что мы подключаем его через порт USB. Последнее очень часто встречается в ноутбуках, особенно небольших, которые не всегда имеют встроенную карту Ethernet. Также, чтобы иметь возможность использовать адаптер Wi-Fi с большей емкостью и, таким образом, иметь лучшее покрытие, чтобы иметь возможность подключать другие устройства независимо от расстояния, поскольку у них обычно лучшая антенна.
Но в дополнение к этим физическим адаптерам у нас также может быть виртуальные сетевые адаптеры . Вот что происходит, если мы используем виртуальную машину, например VMWare. Поэтому иногда мы видим в Windows больше адаптеров, чем есть на самом деле. Иногда мы не знаем, почему это происходит, и это может быть причиной.
Это делает интересным или даже необходимым удалить адаптеры от нашей команды, чтобы решить определенные проблемы или улучшить связь. Иногда возникают конфликты с драйверами или с обнаруженной установкой. Это вынуждает нас переустанавливать их, но мы также можем устранить их, чтобы не было проблем с другими или если мы не собираемся использовать их напрямую.
Удалить сетевые адаптеры в Windows очень просто. Причин может быть несколько. Мы рассказали о примере конфликта с драйверами. Но также может быть, что мы просто хотим, чтобы наше оборудование было «чище» и что сетевые адаптеры которые мы не используем или даже виртуальные, не появляются. Например, если мы купили USB-адаптер Wi-Fi, чтобы иметь большую мощность, чем тот, который встроен в материнскую плату, и мы хотим исключить последний.
Используйте диспетчер устройств
Для этого нам нужно перейти в Пуск, написать Диспетчер устройств и, оказавшись внутри, зайти в Cеть переходники. Там мы увидим все, что мы настроили, и мы увидим, какой из них или который мы хотим удалить. Мы должны щелкнуть второй кнопкой мыши поверх соответствующей и щелкнуть Удалить .

Этот процесс очень простой и быстрый. Нам придется повторять это столько раз, сколько необходимо, чтобы стереть все сетевые адаптеры, физические или виртуальные, которые мы хотим удалить из Windows. Если в будущем мы будем заинтересованы в том, чтобы они снова стали доступны, нам придется установить их снова.
Удалите сетевой адаптер из настроек
Другой вариант, который у нас есть, – удалить сетевые адаптеры непосредственно из системы. Конфигурация . Там, как и в предыдущем случае, мы можем найти все, что добавили, и удалить те, которые нас не интересуют.

После того, как мы введем «Изменить параметры адаптера», мы должны щелкнуть второй кнопкой мыши на адаптере, который мы хотим удалить. Во многих случаях это не позволяет нам устранить его напрямую, как мы можем видеть на изображении ниже в случае этого виртуального адаптера. Поэтому нам нужно будет нажать на Отключите . Вы должны принять появившееся диалоговое окно.

Используйте командную строку
Третий вариант, который у нас есть для устранения недоступных сетевых адаптеров Windows, – это командной строки . Это характеристика самой системы, с помощью которой мы можем выполнять изменения этого типа.
Этот вариант несколько сложнее, поскольку требует ряда шагов и не так быстр, как два предыдущих. Однако мы объясним все, что необходимо сделать, чтобы удалить адаптеры Ethernet и Wi-Fi. Процесс аналогичен, но нам придется изменить команду.
Надо зайти в Пуск, написать Командная строка и запустите его. Мы также можем использовать для этого Windows PowerShell. Таким образом мы можем выполнить необходимые команды для удаления адаптеров.
Первое, что нужно сделать, это узнать имя сетевого интерфейса . Для этого мы должны выполнить одну из этих двух команд, в зависимости от того, хотим ли мы удалить адаптер Ethernet (LAN) или Wi-Fi (WLAN):
- netsh lan показать профили
- Netsh WLAN показывать анкеты
Когда мы это сделаем, нам нужно будет увидеть сетевую карту, которую мы хотим удалить, и отметить соответствующее имя. Это необходимо для следующего шага, будь то Ethernet или Wi-Fi. Вы должны выполнить одну из этих двух команд:
- netsh lan удалить профиль interface = »InterfaceName»
- netsh wlan удалить профиль interface = »InterfaceName»
Короче говоря, это варианты, которые нам нужно исключить сетевой адаптер в Windows – физический или виртуальный. Мы видели разные альтернативы, хотя любая из них была бы полезна для нашей цели. Если мы видим, что адаптер не работает, что он создает какой-то конфликт, мы всегда можем его устранить. Также, если мы просто заинтересованы в чистоте оборудования и в том, что определенные виртуальные или физические адаптеры, которые мы никогда не используем, не появляются.
What is Netsh?
Netsh is a command-line scripting utility that allows you to, either locally or remotely, display or modify the network configuration of a computer that is currently running. Netsh also provides a scripting feature that allows you to run a group of commands in batch mode against a specified computer. Netsh can also save a configuration script in a text file for archival purposes or to help you configure other servers.
Using Netsh
View your TCP/IP settings
netsh interface ip show config
Here is an example of command output:
Configuration for interface "Local Area Connection 1"
DHCP enabled: Yes
InterfaceMetric: 1
DNS servers configured through DHCP
WINS servers configured through DHCP
Configuration for interface "Local Area Connection 2"
DHCP enabled: No
IP Address: 192.168.0.20
SubnetMask: 255.255.255.0
InterfaceMetric: 1
Statically Configured DNS Servers: None
Statically Configured WINS Servers: NoneReset the TCP/IP Stack
netsh interface ip reset log.txt
A common use of netsh is to reset the TCP/IP stack to default, known-good parameters, a task that in Windows 98 required reinstallation of the TCP/IP adapter. In this mode you must provide a log file, which will be filled with what values netsh affected.
Delete arp cache
netsh interface ip delete arpcache
Deletes the arp cache entries for all available adapters (including the dial up adapter). Works well with DSL if you are able to ping the loopback address, and your own IP but nothing else.
Configure your computer’s IP address and other TCP/IP related settings
netsh interface ip set address name="Local Area Connection" static 192.168.0.20 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.1 1
This command configures the interface named Local Area Connection with the static IP address 192.168.0.20, the subnet mask of 255.255.255.0, and a default gateway of 192.168.0.1
Configure your NIC to automatically obtain an IP address from a DHCP server:
netsh interface ip set address "Local Area Connection" dhcp
netsh interface ip set dns "Local Area Connection" static 192.168.0.200
netsh interface ip set wins "Local Area Connection" static 192.168.0.200
Configure your NIC to dynamically obtain it’s DNS settings:
netsh interface ip set dns "Local Area Connection" dhcp
Import/Export your TCP/IP settings
netsh -c interface dump > c:\\MySettings.txt
netsh -f c:\\MyAnotherSettings.txt
Configure firewall
Enable/Disable Windows firewall
netsh firewall set opmode mode=disable
netsh firewall set opmode mode=enable
Add Ports to the Exception List
netsh firewall add portopening TCP 3234 MyTCPPort
netsh firewall add portopening UDP 7365 MyUDPPort
Add applications to exceptions list
netsh firewall add allowedprogram c:\MyProgram.exe
Again if we look at the exceptions list, MyProgram.exe has been added.
netsh firewall show allowedprogram
Show network parameters
netsh diag show adapter
Displays all of the Adapters.
netsh diag show all
Displays all categories.
netsh diag show client
Displays all network clients.
netsh diag show computer
Displays computer information.
netsh diag show dhcp
Displays the DHCP servers for each adapter.
netsh diag show dns
Displays the DNS servers for each adapter.
netsh diag show gateway
Displays the default gateway servers for each adapter.
netsh diag show ieproxy
Displays Internet Explorer’s server name and port number.
netsh diag show ip
Displays the IP address for each adapter.
netsh diag show mail
Displays the mail server name and port number.
netsh diag show modem
Displays all modems.
netsh diag show news
Displays the news server name and port number.
netsh diag show os
Displays operating system information.
netsh diag show test
Displays all categories and performs all tests
netsh diag show version
Displays the Windows and WMI version.
netsh diag show wins
Displays the primary and secondary WINS servers for each adapter.