Fix “Page not found” and other website errors by clearing the DNS cache
Are you having trouble accessing certain websites? Try flushing your DNS cache! If the IP address of a website you’ve recently visited has changed since the last time you accessed it in your browser, you might see a “Page not found” error until your DNS resolver cache is cleared. While this cache (which is different from your web browser’s cache) also clears automatically, doing a manual DNS flush will instantly clear those old stored addresses, which may restore your access to your favorite website. This wikiHow guide will show you the easiest ways to flush your DNS cache on a Windows or Linux PC, Mac, and Chromebook.
Things You Should Know
- If you can’t access a particular website or recently made some network changes, flushing your DNS can be a helpful troubleshooting step.
- If you’re using Windows, flush your DNS using the command ipconfig /flushdns.
- On the latest versions of macOS, run sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder to clear the cache.
- Rebooting your computer will also flush the DNS cache automatically.
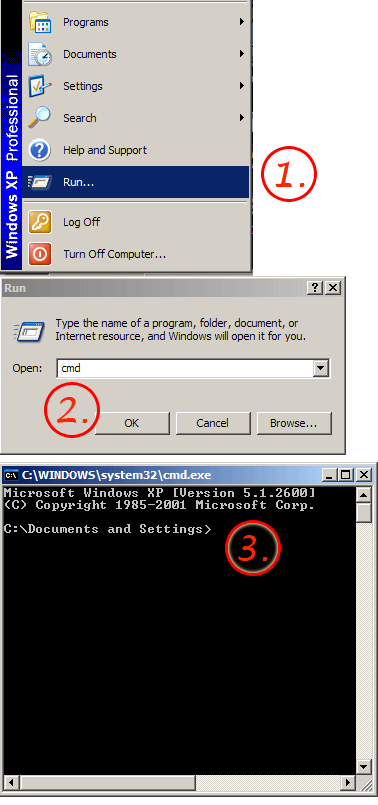
- Press the Windows key on your keyboard and type cmd.
- Right-click Command Prompt in the search results.
- Click Yes to confirm.
- Type ipconfig /flushdns at the prompt and press . This immediately flushes your PC’s DNS cache.
If you just want to see the contents of your DNS cache without flushing it, run the command ipconfig /displaydns instead. This command also displays entries from your hosts file.If your PC is a part of an Active Directory network, you may also need to run the command ipconfig /registerdns if you can’t resolve other hostnames on your network.If you’re still having trouble accessing websites after clearing your DNS cache, you may also need to clear your browser cache. - If you just want to see the contents of your DNS cache without flushing it, run the command ipconfig /displaydns instead. This command also displays entries from your hosts file.
- If your PC is a part of an Active Directory network, you may also need to run the command ipconfig /registerdns if you can’t resolve other hostnames on your network.
- If you’re still having trouble accessing websites after clearing your DNS cache, you may also need to clear your browser cache.
- Open a new Terminal window. If you’re logged in on your Linux desktop, you can press Ctrl + Alt + T to open a new Terminal quickly.
- Run the DNS flush command for your Linux variant. The command you’ll use will be different depending on which version of Linux you’re using:
Ubuntu & Debian:Type sudo systemd-resolve –flush-caches and press Enter. In newer version of Ubuntu you may have to use command sudo resolvectl flush-caches instead.To make sure the command worked, run the command sudo systemd-resolve –statistics to make sure the cache is empty. In newer version of Ubuntu you may have to use command sudo resolvectl statistics instead.
RedHat & CentOS:Type systemctl restart dnsmasq.service and press Enter. You won’t see any confirmation or errors, so don’t worry if you don’t get any feedback. - Ubuntu & Debian:Type sudo systemd-resolve –flush-caches and press Enter. In newer version of Ubuntu you may have to use command sudo resolvectl flush-caches instead.To make sure the command worked, run the command sudo systemd-resolve –statistics to make sure the cache is empty. In newer version of Ubuntu you may have to use command sudo resolvectl statistics instead.
- Type sudo systemd-resolve –flush-caches and press Enter. In newer version of Ubuntu you may have to use command sudo resolvectl flush-caches instead.
- To make sure the command worked, run the command sudo systemd-resolve –statistics to make sure the cache is empty. In newer version of Ubuntu you may have to use command sudo resolvectl statistics instead.
- RedHat & CentOS:Type systemctl restart dnsmasq.service and press Enter. You won’t see any confirmation or errors, so don’t worry if you don’t get any feedback.
- Type systemctl restart dnsmasq.service and press Enter. You won’t see any confirmation or errors, so don’t worry if you don’t get any feedback.
- Go to chrome://net-internals in your browser. This opens a page where you can access a few handy network troubleshooting tools.
- Click in the left panel. Now you’ll see the DNS Lookup page, where you can look up any domain or host name. You’ll also see a button below this option to clear your host cache.
- Click Clear host cache. This flushes the DNS cache in Chrome (or on your Chromebook).
Don’t be alarmed if you don’t see a prompt or confirmation, as everything happens quietly in the background.If you’re still having trouble accessing websites, you can also try clearing your browser cache, - Don’t be alarmed if you don’t see a prompt or confirmation, as everything happens quietly in the background.
- If you’re still having trouble accessing websites, you can also try clearing your browser cache,
Add New Question
- Why do some websites work and others cannot be found?
Your wifi firewall or the country may have some have censorship. Change your VPN to see if that works. - How can I flush a D.N.S. PC laptop or mobile device?
On Windows, open Command Prompt and after the prompt, without the quotes, type in “ipconfig/flushdns”.
See more answers
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
- All devices clear their DNS caches regularly without any human intervention, so you shouldn’t have to flush your DNS cache often.
- Websites may take a bit longer to load the first time you access them after flushing the DNS cache.
Show More Tips
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
References
To flush your Windows computer’s DNS, start by clicking the Windows logo in the bottom left corner of your screen. Then, type “command prompt” into the search box, and select the Command Prompt app, which should be the top icon in the Start window. Next, enter “ipconfig /flushdns,” and press Enter. Finish by restarting your web browser. For tips on how to flush your DNS on a Mac, read on!
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 1,971,358 times.
Reader Success Stories
Команда IPCONFIG используется для отображения текущих настроек протокола TCP/IP и для обновления некоторых параметров, задаваемых при автоматическом конфигурировании сетевых интерфейсов при использовании протокола Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)..
Формат командной строки:
Параметры командной строки:
/? – Вывод справочного сообщения
/all – Вывод подробных сведений о конфигурации.
/release – Освобождение адреса IPv4 для указанного адаптера.
/release6 – Освобождение адреса IPv6 для указанного адаптера.
/renew – Обновление адреса IPv4 для указанного адаптера.
/renew6 – Обновление адреса IPv6 для указанного адаптера.
/flushdns – Очистка кэша сопоставителя DNS.
/registerdns – Обновление всех DHCP-аренд и перерегистрация DNS-имен
/displaydns – Отображение содержимого кэша сопоставителя DNS.
/showclassid – Отображение всех допустимых для этого адаптера идентификаторов классов DHCP.
/setclassid – Изменение идентификатора класса DHCP.
/showclassid6 – Отображение всех допустимых для этого адаптера идентификаторов классов DHCP IPv6.
/setclassid6 – Изменение идентификатора класса DHCP IPv6.
адаптер – Имя подключения (можно использовать знаки подстановки * и ? )
Изменение сетевых настроек с помощью команды IPCONFIG, в основном, применимо к тем сетевым адаптерам, которые настроены на автоматическое
конфигурирование с использованием службы динамической настройки основных параметров на сетевом уровне DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
или службы автоматической настройки приватных IP – адресов APIPA (Automatic Private IP Addressing).
Если в параметрах командной строки IPCONFIG используется имя адаптера, содержащее пробелы, то оно должно заключаться в двойные кавычки.
Если имя содержит символы русского алфавита, то оно должно быть представлено в DOS-кодировке.
Для имен адаптеров применимо использование символа * в качестве шаблона:
* – любое имя
Локальн* – имя адаптера начинается с “Локальн”
*сети* – имя адаптера содержит строку “сети”
Примеры использования ipconfig. exe
ipconfig – отобразить базовые сетевые настройки для всех сетевых адаптеров, присутствующих в системе.
ipconfig /all – отобразить подробную информацию о настройках всех сетевых адаптеров, присутствующих в системе.
ipconfig /renew “Подключение по локальной сети 2” – обновить сетевые настройки, полученные от DHCP – сервера только для сетевого подключения с именем “Подключение по локальной сети 2”.
ipconfig /release *локальной* – обновить сетевые настройки, полученные от DHCP – сервера для всех сетевых подключений, в имени которых присутствует строка “локальной”
ipconfig /release “Подключение по локальной сети 2″ – освободить сетевые настройки, полученные от DHCP – сервера только для сетевого подключения с именем ” Подключение по локальной сети 2″.
ipconfig /dysplaydns – вывести на экран содержимое кэш службы разрешения имен DNS ( службы DNS-клиент).
ipconfig /flushdns – очистить содержимое кэш службы разрешения имен DNS
ipconfig /showclassid “Подключение по локальной сети” – отобразить все допустимые для этого сетевого подключения идентификаторы классов DHCP.
ipconfig /setclassid “Local Area Connection” TEST – установить для адаптера с именем “Local Area Connection” идентификатор класса DHCP “TEST”.
ipconfig /setclassid6 “Local Area Connection” TEST – установить для адаптера с именем “Local Area Connection” идентификатор класса DHCPv6 “TEST”.
Если для параметра setclassid или setclassid6 не указан идентификатор класса, то существующий идентификатор класса будет удален.
Наиболее часто используется команда ipconfig /all, позволяющая получить подробные сведения о сетевых настройках. Отображаются сведения о настройке протокола IP и о настройках
сетевых адаптеров. Пример сведений о настройках IP:
Настройка протокола IP для Windows
Имя компьютера . . . . . . . . . : comp0
Основной DNS-суффикс . . . . . . :
Тип узла. . . . . . . . . . . . . : Смешанный
IP-маршрутизация включена . . . . : Нет
WINS-прокси включен . . . . . . . : Нетipconfig.exe
b-node (b) – Использует только широковещательную регистрацию и просмотр имен.
p-node (p) – использует только соединения точка-точка для просмотра и регистрации имен.
m-node (m) и h-node (h) – смешанные типы, использующие как широковещательные сообщения, так и обращение к серверам имен.
Компьютеры под управлением Windows представляют собой узлы h-node или узлы смешанного типа, использующие WINS (NBNS) сервер для регистрации и просмотра имен, и
используют широковещательные запросы, если сервер не доступен.
Пример отображаемой конфигурации сетевого адаптера :
Ethernet adapter Подключение по локальной сети :
DNS-суффикс подключения . . . . . :
Описание. . . . . . . . . . . . . : Realtek 8139d Adapter #2
Физический адрес. . . . . . . . . : 00-14-02-7B-ED-67
DHCP включен. . . . . . . . . . . : Да
Автонастройка включена. . . . . . : Да HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESystemCurrentControlSetServicesTcpipParametersInterfacesGUID адаптераIPAutoconfigurationEnabled0
Автонастройка IPv4-адреса . . . . : 169.254.254.18(Основной)
Локальный IPv6-адрес канала . . . : fe80::7c22:e7f8:3a71:8249%16(Основной)
IPv4-адрес. . . . . . . . . . . . : 10.10.11.77(Основной)
Маска подсети . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.224.0
Аренда получена. . . . . . . . . . : 2 марта 2015 г. 22:44:48
Срок аренды истекает. . . . . . . . . . : 3 марта 2015 г. 2:31:27
Основной шлюз. . . . . . . . . : 10.10.11.1
Код класса DHCPv4. . . . . . . . . . : TEST
DHCP-сервер. . . . . . . . . . . : 10.10.11.11 –
Следующие 2 параметра (идентификатор участников DHCP – DUID и идентификатор арендованного адреса IAID) присутствуют при автоматическом конфигурировании настроек протокола IPv6 . В крупных сетях могут присутствовать несколько серверов DHCPv6. При автоматическом конфигурировании сетевого адаптера, все они получают от клиента специальный запрос DHCP REQUEST. Каждый из них проверяет, ему ли был направлен запрос. Сервер не приступает к обработке пакетов с DUID, отличающимся от его собственного. При совпадении DUID, сервер помечает адрес как присвоенный и возвращает ответ DHCP REPLY. На этом обработка запроса завершается.
IAID – это специальный идентификатор арендуемого IPv6-адреса длиной 4 байта. Клиенту выделяется адрес на время, определенное сервером (срок аренды). Когда предпочитаемый срок действия адреса заканчивается, клиент отправляет серверу пакет DHCP RENEW с запросом на продление этого срока. В сообщение включается идентификатор IAID, код которого также хранится в базе данных DHCP сервера. Если сервер готов продлить срок действия адреса, он отправляет ответ DHCP REPLY и клиент получает возможность использования арендованного адреса без повторного получения настроек.
IAID DHCPv6 . . . . . . . . . . . : 234890384
DUID клиента DHCPv6 . . . . . . . : 00-01-00-01-14-E2-78-C0-00-0C-1E-7C-29-E3
DNS-серверы. . . . . . . . . . . : 94.25.128.74
94.25.208.74
NetBios через TCP/IP. . . . . . . . : Включен
Вывод команды IPCONFIG, как правило, не помещается на экране, поэтому для постраничного отображения результатов можно использовать команду more в цепочке с командой IPCONFIG:
При необходимости, результаты можно записать в текстовый файл, используя перенаправление вывода:
start “winword” winword.exe %TEMP%ipconfig-all.txt
Первая команда записывает результаты выполнения IPCONFIG в текстовый файл ipconfig-all.txt каталога временных файлов, путь которого определяется значением переменной TEMP, а вторая – открывает этот файл с помощью winword.exe. При открытии, приложение Microsoft Word выдаст запрос на преобразование файла и предложит выбрать исходную кодировку текста – Кириллица (DOS) .
Также можно воспользоваться стандартным буфером обмена Windows, записав в него вывод результатов команды IPCONFIG. Для этого нужно выполнить ее в цепочке с командой clip
Результат выполнения команды будет записан в буфер обмена Windows, после чего в используемом редакторе (Блокнот, Wordpad, Word, OpenOffice Writer) можно выполнить вставку из буфера обмена (нажмите Ctrl+V или Shift+Insert)
Весь список команд CMD Windows
A list of Windows DOS ipconfig commands and networking commands available from the Command Prompt in Windows. Such as ipconfig, ping, tracert, and more. These command line tools are used to troubleshoot internet issues and local networking hangups. Please comment below if you have any questions.
Ipconfig Commands
Display Full ipconfig Configuration:
Release All IP Addresses:
Renew All IP Addresses:
Display DNS Resolver Cache:
Clear DNS Resolver Cache:
Fresh Register DNS Connections:
Ping Commands
Ping IP Address:
Continuous Ping: ping -t 127.0.0.1
Ping X Amount of Times: ping -n 10 127.0.0.1
Ping A Sized Packet: ping -l 1500 127.0.0.1
Ping Timeout Limit: ping -w 5000 127.0.0.1
Resolve Host Name: ping -a 127.0.0.1
Networking Commands
Get a sites IP:
Displays all active TCP connections:
Find your MAC Address:
Display other devices on network:
Winsock Reset: netsh winsock reset
TCP/IP reset: netsh int ip reset resetlog.txt
The ipconfig command is used to find out your current local IP address, default gateway, TCP/IP settings and more. With IPCONFIG you can not only find out your IP Address, find your default gateway and find your subnet mask, you can release and renew, resolve the DNS, troubleshoot internet connections and more. This is a very handy network tool for finding your local IP address as well as many other secrets.
Ipconfig cmd explained
To display all of your current IP information for all adapters. With ipconfig /all you can also find out your DNS Server and MAC Address. This will show your ethernet adapters full TCPIP configuration for all adapters on your Windows computer. You can find out your own IP Address as well as your default gateway.
Use IPCONFIG release to release your current IP information and obtain a new IP Address from the DHCP server.
Use to IPCONFIG renew to renew your IP Address if you have it set to obtain IP Address automatically.
This shows your current DNS resolver cache logs. DNS caching basically tells your computer to store the DNS locally. Meaning it now knows what website name is attached to what IP address and it can load faster using the DNS cache instead of having to resolve to it.
The Flush DNS Command flushes or clears your current DNS resolver cache logs. If a website were to switch hosts or get a new IP address, yet still have an old DNS cache, it would direct you to a no longer working site. In this case, you would have to flush the DNS to obtain fresh information upon your next visit. This can happen if a website has a dynamic IP.
The register DNS command updates the DNS settings on the Windows computer. It doesn’t just access the local DNS cache, it initiates communication with the DNS server and the DHCP server so it can re-register the network address. You can use this for troubleshooting problems with connection to the ISP (Internet Service Provider), like failing to obtain a dynamic IP address from the DHCP Server or failing to connect to the ISP DNS server.
If you ever wonder “what your IP Address is” you would run an ipconfig as shown above. Note, this will only show you your local network private IP address and not your WAN address. If you need to find your IP address, default gateway(router login) or subnet mask, then ipconfig is the command prompt tool to use. These numbers can be very helpful when troubleshooting your internet connection. If you have changed your settings, but they are not taking place, you may try a ipconfig release and renew. If you’re having problems resolving to a website, you may try flushing your DNS Resolver Logs.
Ping cmd switches
In all of these examples “xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx” is an example of a Domain Name or an IP Address. You must fill those out yourself.
ping xxx.xxx.xx.xx -t Continuous Ping – It will keep on pinging forever until you hit Ctrl + C to stop it. This can be great for troubleshooting intermittent connections. Just open up a Command Prompt(or 3) and run the continuous ping command on a site like Google.com to see when you’re dropping packets. I would also run one on your router and on another site like site.com for a better data sample control group. What I mean by this is if you’re pinging your website and losing packets yet not losing packets to Google, you know the problem is somewhere between you and your hosting company. If you are losing packets to your own router, the problem is with your local network. It could be the cat5 cable, your router or your hardware. You will have to do further troubleshooting to figure out where the problem is. To check if it is your router, do the same ping from another computer and if it is fine, it is your hardware or cable and not the router. You get the idea, use your head, be logical, troubleshoot.
ping xxx.xxx.xx.xx -n 10 Number of Pings – The N Switch is simply for setting the number of pings. By default, the ping cmd sends out 4 packets at 32 bytes each.
ping xxx.xxx.xx.xx -l 1500 Size of Packet – By default, the packets sent are a small 32 bytes. You can set your own size up to the max 65500 bytes. This can really help with stress testing your local network.
ping xxx.xxx.xx.xx -w 5000 Time Out – This is in milliseconds. The timeout by default is 4,000 milliseconds which amounts to 4 minutes. Just seeing if you were still paying attention. It really is only 4 seconds.
ping -a xxx.xxx.xx.xx Resolves Hostname Address – This is a great one if you are helping someone else and need to find out what router model they are using. You can resolve the host of an IP Address with this command. Try pinging your router or your local computer with it. ping -a 127.0.0.1. Note that this switch will only work in front of the IP Address.
The Ping command is a network tool used to determine if you are able to send packets between your network computer on the internet to another computer without losing packets along the way. By doing this you can determine if you’re online or if a website is down. It also calculates round trip time and Time to Live. This can let you know if your NIC card is working properly and if you can reach your router or modem. It is an invaluable command for troubleshooting internal network and external internet connections.
Basic Windows Network Tools
With Trace route you can trace the path your packets take across the internet from you to your destination. Along the way you can determine the time from hop to hop. You can identify server problems and latency with this tool. It really helps see where the failure is between you and a destination. It may very well even be out of your hands.
nslookup site.com nslookup xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx nslookup is a way to get the IP address for a domain name. You can also do a reverse lookup from Domain Name to IP Address. It can be a way to find out if your DNS is properly working or if the site is having problems. You can obtain an IP from a site and try to visit the IP directly, bypassing the Domain Name Servers that would usually resolve the Domain name to IP name.
netstat can be used to view your active network connections and TCP/IP connections. You can determine what ports are open and being used, what programs are using your ports and what kind of TCP and UDP connections are present. Looking in here for the first time may scare the hell out of you.
netstat Switches Displays all active TCP connections. And TCP / UDP ports. Displays ethernet statistics. Displays all active programs that are listening.
How do I find my MAC Address you might ask? If you open up the command prompt you simply type getmac to get your computers local MAC address.
To get the MAC address of your router or other devices on your local network, you may use the arp -a command. With this information, you can find out what type of router you are connected to by using this website. Simply plug in the MAC Address of your default gateway(found from IPCONFIG) and you can get the brand name of your router without looking at it. Pretty neat. Helpful in some situations.
The best command prompt trick is how easy it is to access it. On Windows XP, Vista, Windows 7 or Windows 8 just press and hold the Windows Key + R on your keyboard. The other way to access the DOS Command prompt is to simply go to your Windows Start menu, Then go to Run. When the little box pops up you type in cmd. Once the Black Command Prompt pops up you can type any of these commands in and have some fun!
Networking / Beginners
How long entries are stored in the resolver cache depends on the Time to Live (TTL) value assigned to the record by the originating server. To view current records and see the remaining TTL value for each record, in an elevated command prompt, type ipconfig/displaydns. These values are given as the number of seconds that a particular record can remain in the cache before it expires. These values are continually being counted down by the local computer. When the TTL value reaches zero, the record expires and is removed from the resolver cache.
Occasionally, you’ll find that the resolver cache needs to be cleared out to remove old entries and enable computers to check for updated DNS entries before the normal expiration and purging process takes place. Typically, this happens because server IP addresses have changed and the current entries in the resolver cache point to the old addresses rather than the new ones. Sometimes the resolver cache itself can get out of sync, particularly when DHCP has been misconfigured.
In most cases, you can resolve problems with the DNS resolver cache by either flushing the cache or reregistering DNS. When you flush the resolver cache, all DNS entries are cleared out of the cache and new entries are not created until the next time the computer performs a DNS lookup on a particular host or IP address. When you reregister DNS, Windows Vista attempts to refresh all current DHCP leases and then performs a lookup on each DNS entry in the resolver cache. By looking up each host or IP address again, the entries are renewed and reregistered in the resolver cache. You’ll generally want to flush the cache completely and allow the computer to perform lookups as needed. Reregister DNS only when you suspect that there are problems with DHCP and the DNS resolver cache.
- Start an elevated command prompt.
- To clear out the resolver cache, type ipconfig/flushdns at the command line.
- To renew DHCP leases and reregister DNS entries, type ipconfig/registerdns at the command line.
- When the tasks are complete, you can check your work by typing ipconfig/displaydns at the command line.
This post mainly introduces the ipconfig command. Learn how to use various ipconfig commands, e.g. ipconfig, ipconfig /all, ipconfig /release, ipconfig /renew, ipconfig /flushdns, ipconfig /displaydns, etc. to find your IP address, release or renew IP address, flush DNS, etc. on your Windows 10/11 computer.
On This Page :
What is ipconfig Command?
ipconfig is short for internet protocol configuration. It is a console application in Windows OS that can display all your current TCP/IP network configuration values like your IP address. It can also flush your DNS (Domain Name System) settings, refresh DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) settings, etc. The ipconfig command is also available in macOS and ReactOS.
Main ipconfig Commands Introduction
You can type the ipconfig command without parameters in the Command Prompt window and press Enter. This command displays the Internet Protocol version IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, subnet mask, and default gateway for all adapters.
The ipconfig command displays the basic TCP/IP configuration for all adapters. To display the full TCP/IP configurations for all adapters on your computer, you can type the ipconfig /all command and press Enter. The ipconfig /all command displays more detailed information than ipconfig clone. It displays your IPv4 address, IPv6 address, DNS servers, MAC address, adapter description, DHCP details, etc.
Ipconfig /release command
This ipconfig command releases the IPv4 address of all network adapters. To release the IPv6 address of all adapters, type the command ipconfig /release6 and press Enter.
The ipconfig /release command sends a DHCP release notification to the DHCP server to force release the current DHCP configuration and IP address, and mark the old client’s IP address as available.
Ipconfig /renew command
After you type the ipconfig /release command to release the old IP address, you can type the command ipconfig /renew and press Enter to request a new IP address for the client. This command will renew the DHCP configuration for all adapters.
Ipconfig /displaydns command
Your computer creates a local cache of all DNS records. The DNS Resolver Cache is used to translate domain names to IP addresses. To check the detailed information of all DNS records, you can type the ipconfig /displaydns command in Command Prompt and press Enter. It will display the DNS record name, type, time to live, data length, section, etc.
Ipconfig /flushdns command
This command can flush and reset the DNS Resolver Cache. When troubleshooting DNS problems, you can use this ipconfig command to clear problematic DNS cache entries and make sure future requests use the fresh DNS information.
Ipconfig /registerdns command
This command refreshes all DHCP leases and registers the DNS names again.
Ipconfig /showclassid command
This ipconfig command displays all the DHCP class IDs for all adapters. Type the ipconfig /showclassid6 command to display all the IPv6 DHCP class IDs. For a specific adapter, add the adapter name at the end of the command.
Ipconfig /setclassid command
Type this command to configure the DHCP class IDs for adapters. For a specific adapter, add the adapter name at the end of the command.
Ipconfig /? command
Display help of the ipconfig commands.
Verdict
In this post, you’ve learned the various ipconfig commands. Now you can use the ipconfig command to check your IP address, use the ipconfig /release and ipconfig /renew commands to release and renew your IP address, use ipconfig /displaydns and ipconfig /flushdns commands to display or reset/flush DNS, etc.
If you have other computer problems, please visit MiniTool Software official website.
Серверы обычно устанавливаются DNS вашим интернет-провайдером. Вы можете изменить его, чтобы повысить скорость интернета или заблокировать некоторые веб-сайты. Другие причины, по которым вам следует внести это изменение, могут заключаться в том, что веб-сайты загружаются медленнее. более длительное использование DNS сервер Общие – хороший метод устранения неполадок для определения проблемы. Независимо от причины, я определенно предлагаю Вы меняете DNS-сервер Ваш.
Вот несколько способов изменить ваш DNS-сервер, но прежде чем вы начнете, важно понять, как работает DNS.

Сколько существует DNS-сервисов?
Многие из них, но некоторые из них стоит знать. Ниже представлены самые популярные из них с их особенностями.
- GoogleDNS. Для большей скорости (8.8.8.8 и 8.8.4.4)
- OpenDNS. Для родительского контроля (208.67.222.222 и 208.67.220.220).
- Нортон КоннектСафеДНС. Подходит для защиты и безопасности от вредоносных программ.
Итак, какой DNS мне подходит?
Зависит от того, для чего вы хотите его использовать. Лучшего DNS-сервера нет. Иногда сторонний DNS хорош для скорости и безопасности. А иногда это DNS вашего интернет-провайдера Подходит для загрузки файлов с соседнего сервера От тебя.
В зависимости от ваших требований вы можете изменить DNS своего компьютера, смартфона или роутера. Посмотрим, как это работает.
Как сменить DNS-сервер
Самый короткий способ изменить ваш DNS-сервер – через командную строку. Вам нужно выполнить только одну команду. Во-первых, вам нужно открыть cmd с правами администратора. Для этого введите cmd в меню «Пуск». Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши значок командной строки и выберите Запуск от имени администратора.
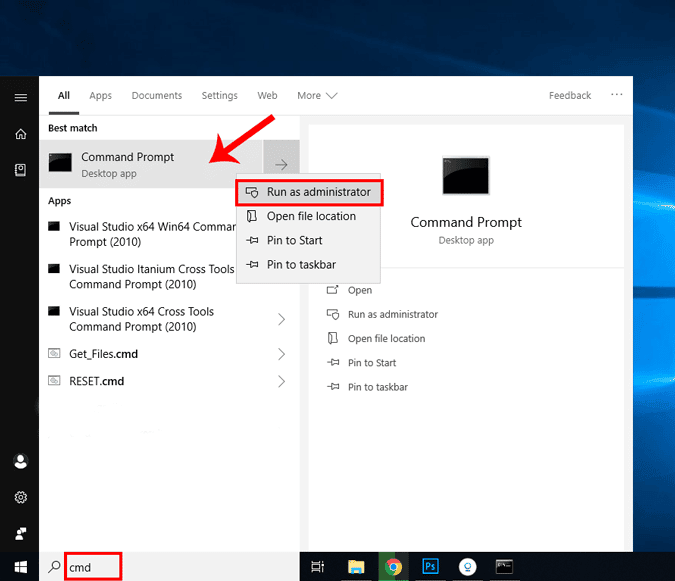
Теперь, когда вы запустите командную строку, нам нужно проверить имя нашего активного сетевого адаптера. Для этого выполните следующую команду.
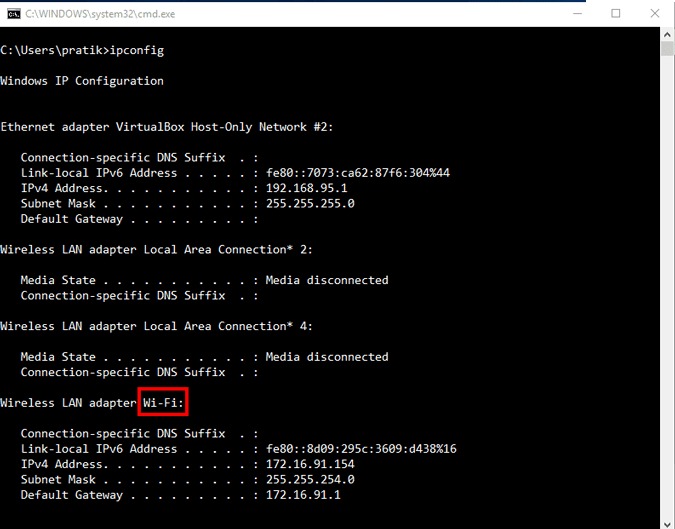
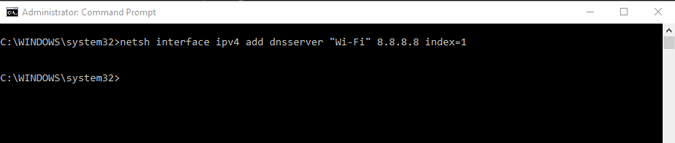
Имя сетевого адаптера – это одно слово, добавленное в конце сетевого адреса. В моем случае «Wi-Fi» находится на конце адаптера беспроводной локальной сети. Итак, имя моего сетевого адаптера – «Wi-Fi». Как только вы получите имя, выполните следующую команду, чтобы изменить DNS-сервер.
netsh interface ipv4 add dnsserver “Wi-Fi” 8.8.8.8 index=1
Здесь Netsh – это встроенная утилита настройки сети Windows. «Wi-Fi» – это имя адаптера, и вы можете заменить его именем своего адаптера, а index = 1 означает первичный DNS-сервер.
Смена DNS-сервера в Windows 10/8/7 – графический интерфейс
Если вы не разбираетесь в командной строке, самый простой способ изменить DNS-сервер – через графический интерфейс. Вам просто нужно зайти в настройки адаптера. Для этого перейдите в меню «Пуск» и введите «Сетевые подключения». Когда появятся результаты поиска, щелкните значок сети.
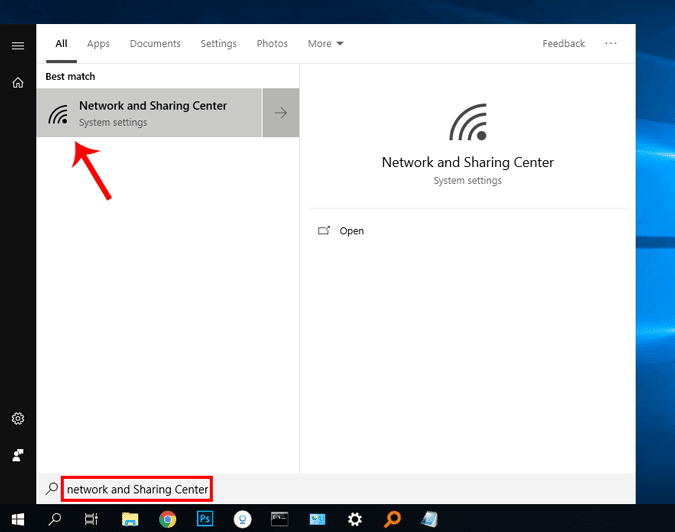
Кроме того, в Windows 10 вы можете быстро открыть Центр управления сетями и общим доступом. Просто щелкните правой кнопкой мыши кнопку «Пуск» и выберите «Сетевые подключения». Вы попадете прямо в окно состояния сети.
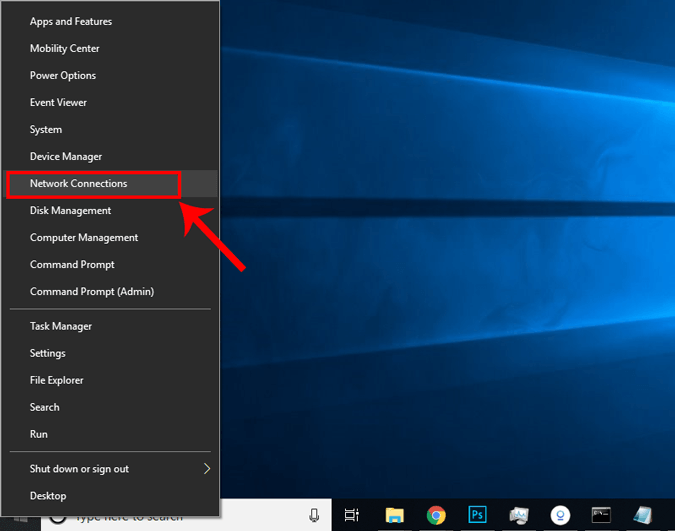
Когда откроется окно «Состояние сети», нажмите «Изменить параметры адаптера».
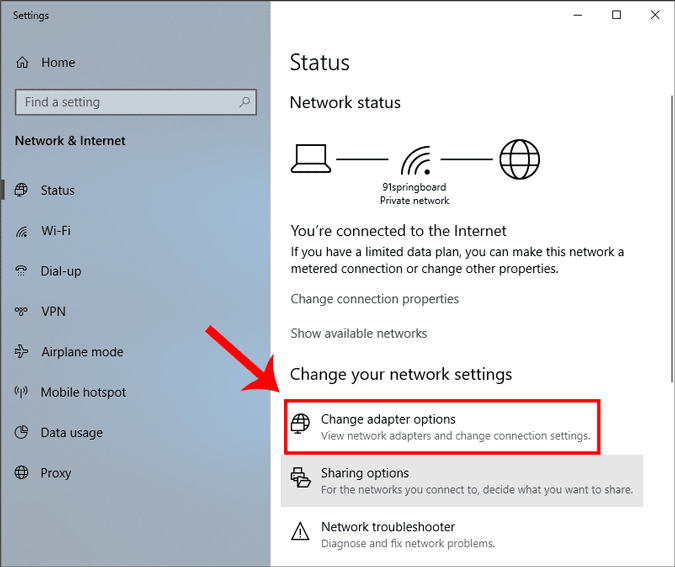
Вы увидите всплывающее окно для сети. Выберите ваше активное соединение. В моем случае это будет «Wi-Fi», но если вы подключены по локальной сети, выберите Ethernet. Щелкните активное соединение правой кнопкой мыши и выберите «Свойства».

Когда вы получите свойства Wi-Fi, выберите «Протокол Интернета версии 4 (TCP / IPv4)». После этого нажмите «Свойства», чтобы открыть настройки IP-конфигурации.
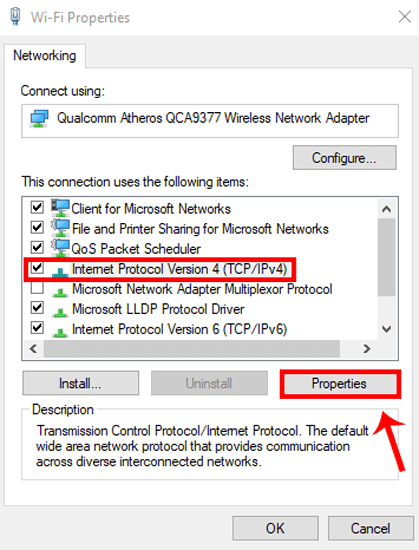
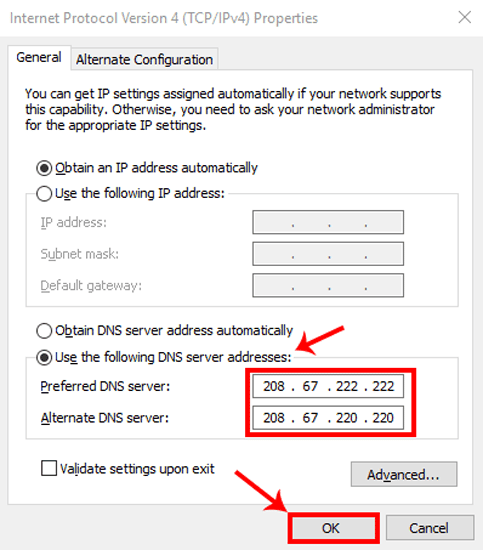
После этого нажмите OK, чтобы сохранить изменения. Вы можете проверить, есть ли у вашего компьютера Использует тот же DNS-сервер Выполнив следующую команду на cmd.
Проблема с обоими методами заключается в том, что вам нужно найти адреса для DNS-сервера. Более того, нет единого окна для ввода адресов DNS и записи предыдущих записей. Если вы часто переключаете DNS, рекомендуется использовать стороннее программное обеспечение, например Перемычка DNS. Это бесплатный и портативный инструмент, поэтому устанавливать его не нужно. Вы можете дважды щелкнуть приложение, чтобы запустить его. Когда откроется окно, вы увидите опцию «Выберите DNS-сервер. Под ним вы увидите раскрывающееся меню с предустановленным списком DNS-серверов. Выберите любой и нажмите «Применить DNS».
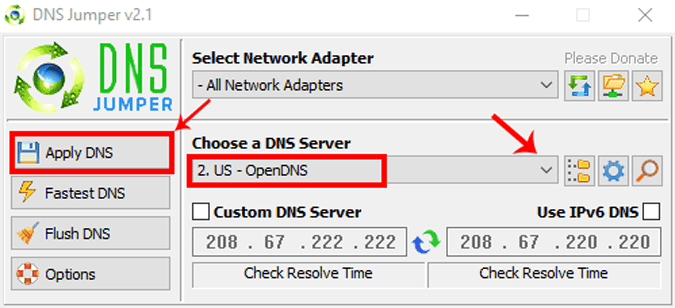
Вы также можете ввести свои собственные DNS-серверы. Чтобы увидеть изменения, вам нужно нажать Flush DNS. В приложении есть много других функций, таких как проверка времени разрешения DNS, применение DNS ко всем адаптерам.
Измените DNS-сервер в Ubuntu.
В Ubuntu процесс смены DNS-сервера чем-то похож на Windows. Вы можете сделать это через командную строку или графический интерфейс пользователя. Самый простой способ сделать это – через графический интерфейс. Вам просто нужно внести некоторые изменения в настройки IP. Для этого щелкните значок сети в правом верхнем углу.
После того, как вы нажмете на значок сети, внизу появится лоток. Щелкните активный сетевой адаптер, чтобы отобразить дополнительные параметры в раскрывающемся списке. Затем нажмите Настройки проводной сети.
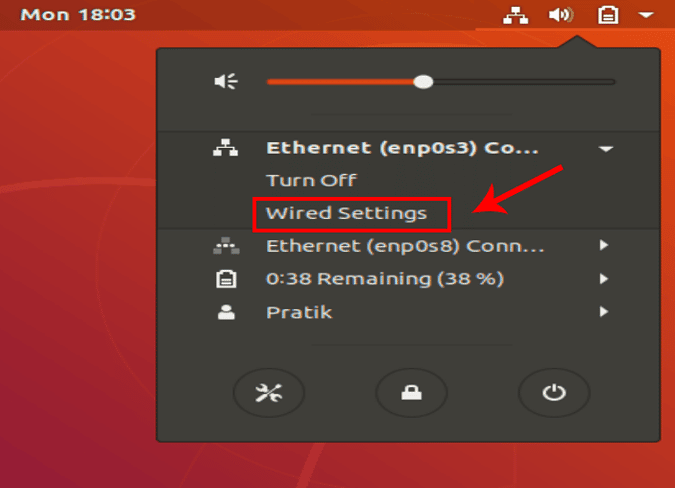
Подождите, пока не появится окно настроек сети. Убедитесь, что вы находитесь на вкладке «Сеть» и переходите к активному адаптеру. Щелкните значок Параметры рядом с адаптером, чтобы просмотреть его конфигурации.
Когда появится всплывающее окно «Настройки проводной сети», перейдите на вкладку IPv4, чтобы изменить настройки IP.
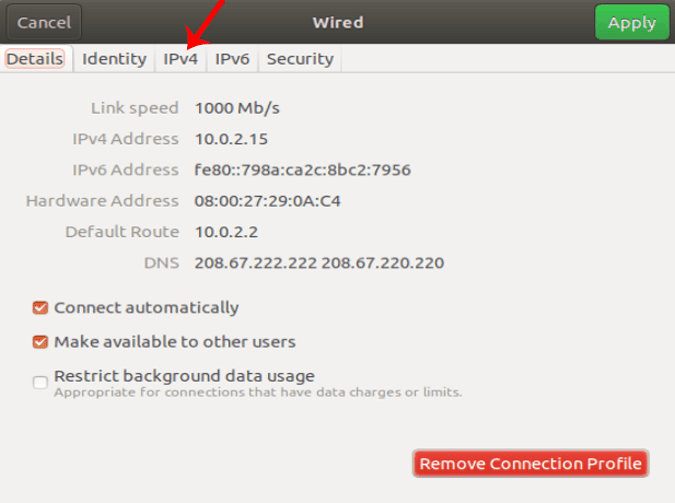
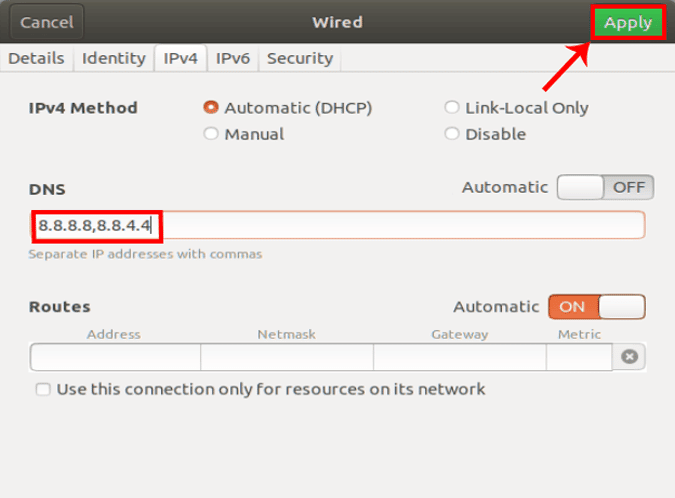
После применения изменений нам необходимо перезапустить сеть, чтобы изменения вступили в силу. Вы можете просто включить и выключить Wi-Fi или запустить эту команду на терминале.
sudo service network-manager restart
Теперь, чтобы проверить, использует ли сетевой адаптер тот же DNS-сервер, выполните следующую команду.
Измените DNS-сервер в macOS.
Если вы используете macOS, изменение DNS аналогично Windows и Ubuntu, но более быстрым способом. Нам нужно изменить настройки сети. Для этого щелкните значок Apple в верхнем левом углу рабочего стола. В раскрывающемся меню выберите Системные настройки.
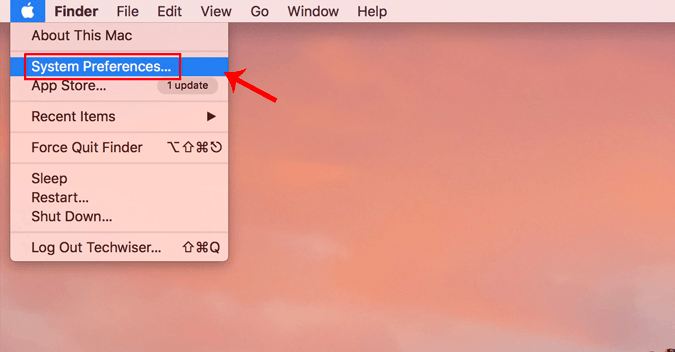
После отображения диалогового окна «Системные настройки» перейдите в «Сеть» и щелкните по нему, чтобы открыть «Настройки сети».

Кроме того, вы также можете нажать Cmd + пробел Чтобы включить поиск Spotlight. Введите «Сеть» в строке поиска и щелкните значок, когда он появится. Это приведет вас прямо к настройкам сети.
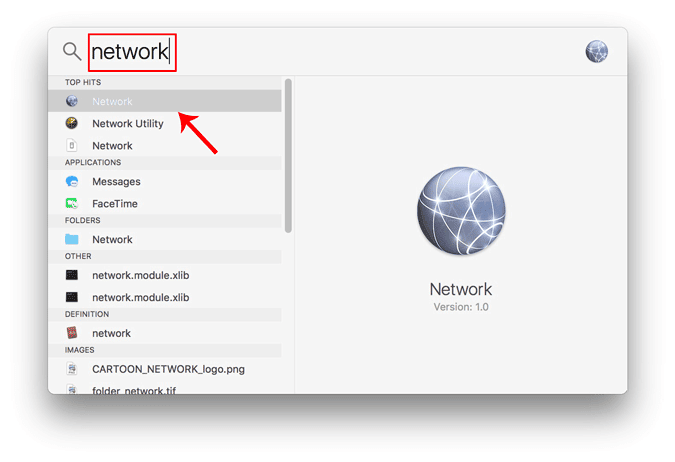
Во всплывающем окне выберите активный сетевой интерфейс. Например, я подключен к Wi-Fi, поэтому моя активная сеть – Wi-Fi. Убедитесь, что вы находитесь на активной вкладке сети, а затем нажмите «Дополнительно».
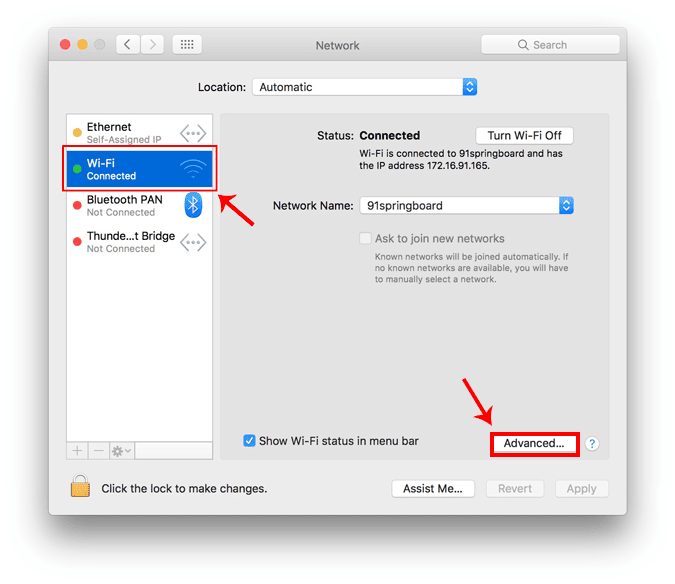
Откроется новое окно с настройками конфигурации для этого адаптера. Перейдите в настройки DNS, щелкнув вкладку DNS.
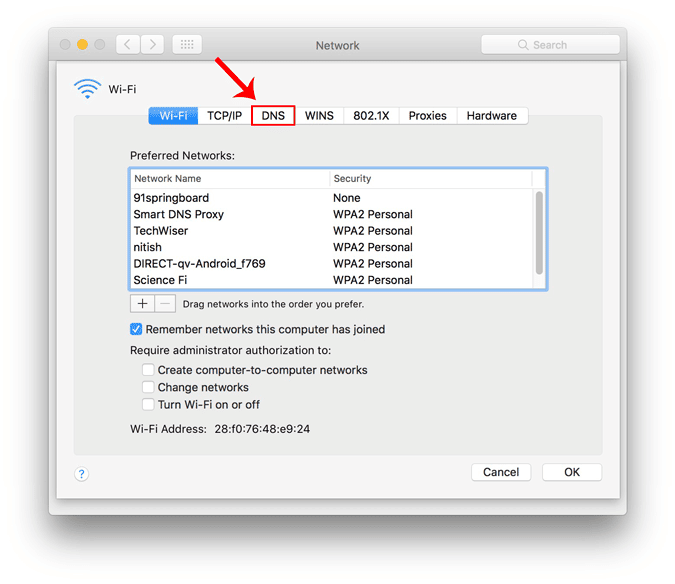
Когда вы перейдете на вкладку DNS, вы увидите кнопку «+» в правом нижнем углу диалогового окна. Нажмите кнопку «+», чтобы добавить DNS-серверы и очистить все предыдущие серверы. Вы можете добавить столько, сколько хотите, нажав кнопку «+». Порядок, в котором вы вводите адреса DNS, будет определять первичный и вторичный серверы DNS. Когда закончите, нажмите OK.
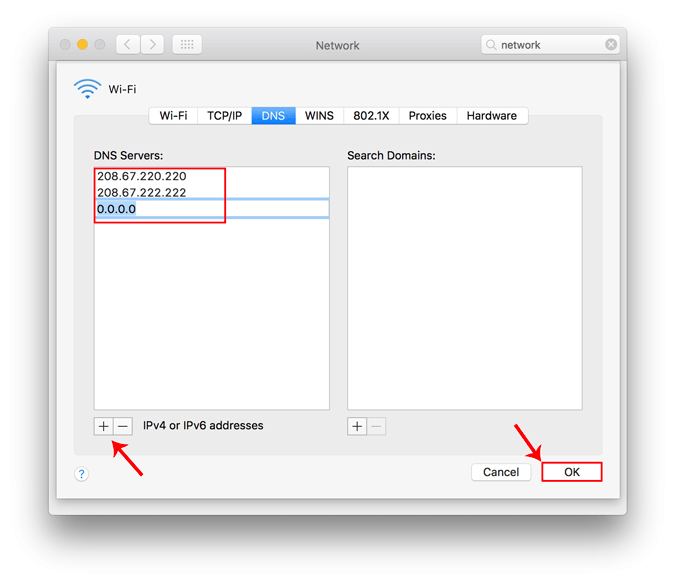
На странице «Параметры сети» нажмите «Применить», чтобы изменения вступили в силу. Перезапустите Wi-Fi, чтобы изменения вступили в силу. Теперь DNS-сервер должен быть тем, который вы выбрали в настройках сети.
Измените DNS-сервер на Android.
В более новых версиях Android у вас есть возможность изменить DNS-сервер изначально. Я использую Note 9 для этой демонстрации. Но шаги по смене DNS-сервера будут такими же, как на большинстве телефонов Android. Нам нужно перейти в меню «Настройки» и открыть «Сеть и подключения». Как только вы окажетесь на этой странице, нажмите «Wi-Fi».
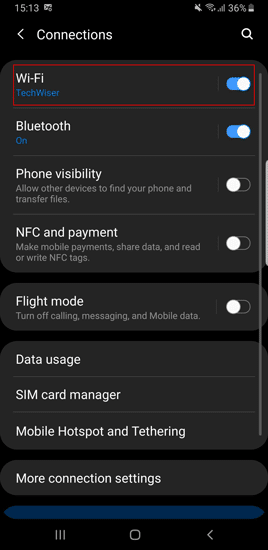
Когда вы находитесь на странице настроек Wi-Fi, вверху вы увидите активное соединение Wi-Fi. Нажмите на него, чтобы получить доступ к конкретной странице конфигурации Wi-Fi.
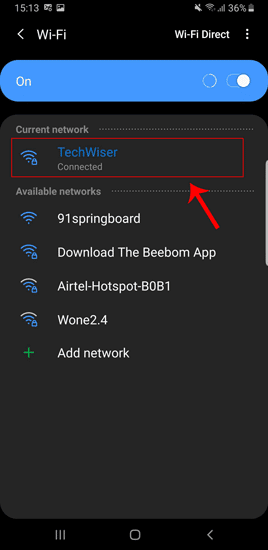
На странице конфигурации Wi-Fi перейдите в Advanced. В общем, он будет внизу всех опций.
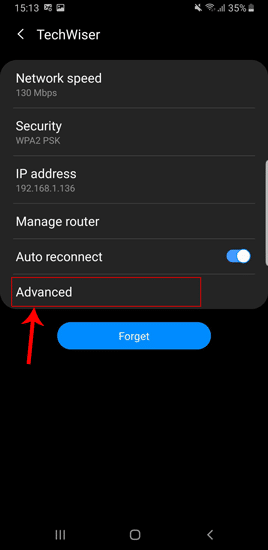
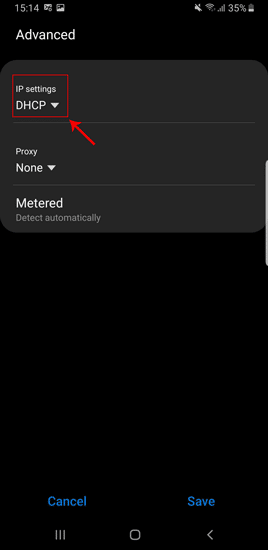
Когда вы нажмете «Дополнительно», вы будете перенаправлены на страницу расширенного раздела. В стандартной версии Android вы увидите всплывающее окно. В любом случае, настройки IP по умолчанию будут установлены на «DHCP». Таким образом, вы не увидите никаких настроек DNS. Вам нужно переключиться на статический, чтобы изменить свой DNS-сервер.
Как только вы переключите настройки IP на статический, вы увидите множество текстовых полей. Перейдите в DNS1 и DNS2. Здесь вы можете ввести свой первичный и вторичный DNS-серверы. Теперь нажмите кнопку «Сохранить», чтобы изменения вступили в силу.
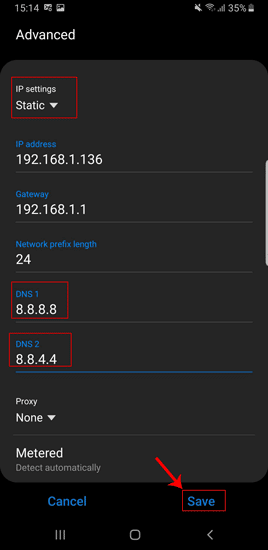
Проблема с этим методом заключается в том, что вы можете установить только 2 DNS-сервера, и они очень специфичны для SSID. Решением может стать стороннее приложение, но большинство из них не работает на Android версии 7 и выше. Если вы используете более раннюю версию Android, например Lollipop, вы можете попробовать приложение Настройки Wi-Fi.
Измените DNS-сервер на iPad / iPhone.
Если вы используете iOS, действия очень похожи на действия для Android. Зайдите в меню настроек, щелкнув значок настроек. Он должен быть в правом нижнем углу экрана в Dock.
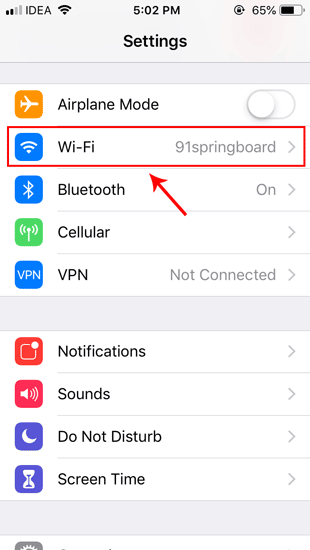
Нажмите Wi-Fi и в разделе «Параметры Wi-Fi» вы увидите сеть Wi-Fi, к которой вы подключены, вверху списка. Когда вы находитесь на странице Wi-Fi, нажмите кнопку «i» рядом с Wi-Fi, к которому вы подключены.
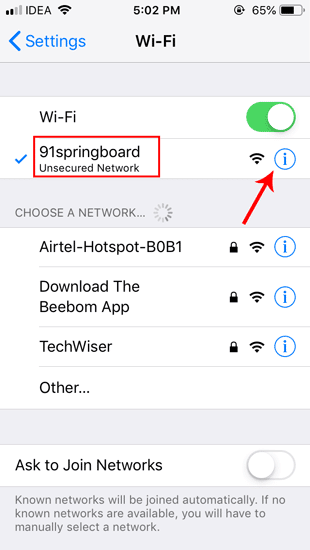
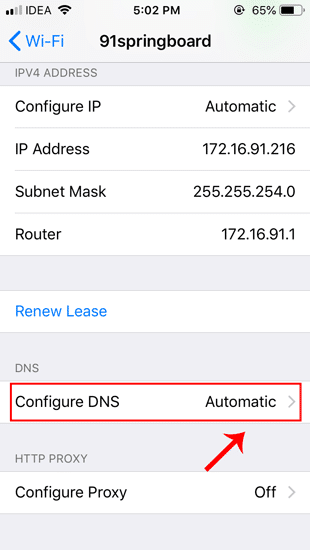
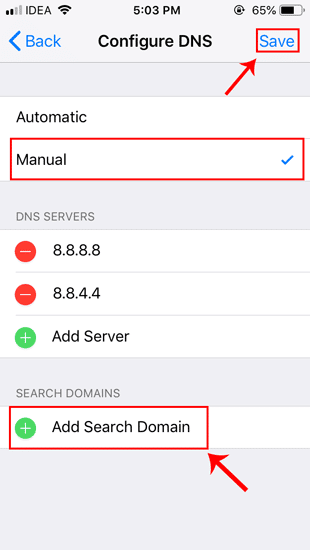
Теперь ваш телефон должен начать использовать настроенный вами DNS-сервер.
Измените DNS-сервер на уровне роутера.
Проблема со всеми вышеперечисленными методами заключается в том, что вы меняете DNS на определенном устройстве. Если у вас есть доступ к маршрутизатору, подумайте об изменении DNS на нем. Таким образом, изменения могут быть применены ко всем устройствам, подключенным к сети. Экономит время и конфигурацию.
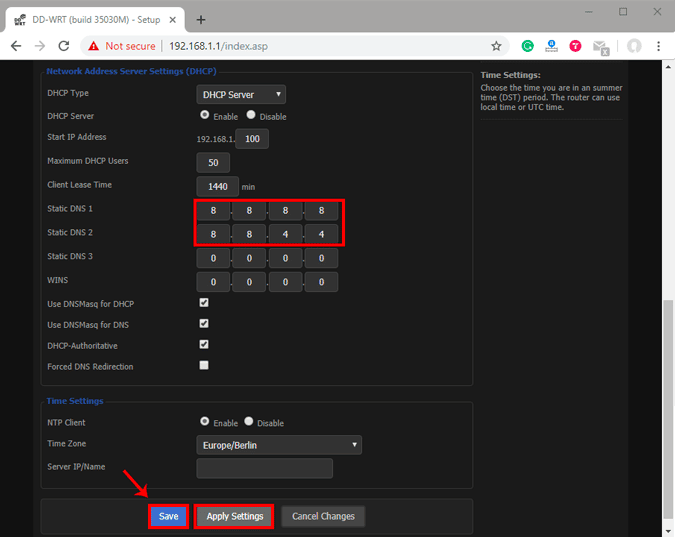
Каждый маршрутизатор отличается и имеет свой пользовательский интерфейс. На моем роутере Netgear с кастомным ПЗУ DD-wrt. Таким образом, шаги будут не идентичны для вас, а скорее похожи. Сначала войдите на веб-портал маршрутизатора. Адрес портала, имя пользователя и пароль часто печатаются за маршрутизатором. Если у вас нет физического доступа к маршрутизатору, URL-адрес шлюза по умолчанию часто будет адресом шлюза вашего ПК. Чтобы найти это, откройте командную строку и введите следующую команду.
После загрузки веб-сайта войдите в систему с учетными данными. Теперь у каждого маршрутизатора свой пользовательский веб-интерфейс, но общая структура осталась прежней. Перейдите на страницу базовой настройки на вкладке настройки.

تغليف
Если у вас есть доступ к роутеру, я рекомендую настроить DNS на роутере. Если у вас нет доступа к маршрутизатору и вы находитесь в офисной сети, второй лучший способ – настроить его локально. После того, как вы настроили DNS на локальном компьютере, он переопределит настройки на вашем маршрутизаторе. Также есть вероятность, что ваше устройство все еще не использует тот же DNS.
The ipconfig command has been around for a long time but somehow most people don’t realize what all of the various ipconfig commands do and how they work. In this Nugget, we’re going to change that by diving into how the ipconfig command works and how it can help you manage your DHCP and DNS client configuration.
Let’s dive right in.
Prerequisites
Running the ipconfig command doesn’t require many prerequisites. As long as you have any recent version of Windows, you’re good to go. This Nugget will also assume you’re on a Windows machine with a dynamically-assigned (DHCP) IP address and DNS client settings.
Viewing Basic IP and DNS Settings with IPConfig Commands
The most basic of ipconfig commands is simply running it without parameters. Open up a command prompt or PowerShell console on your machine and run ipconfig. You will see all of the network interfaces (NICs) installed on your system along with basic IP information.
Take note of the NIC name. The name of the NIC in the below screenshot is called Ethernet.

Viewing basic IP information
Use the ipconfig /all command and you’ll see an increased amount of information namely each NIC’s DHCP configuration and the DNS servers.

Viewing all IP and DNS configuration
Viewing the DNS Resolver Cache
Another popular ipconfig command is ipconfig /displaydns. Using this command, you can find all of the items in your local DNS resolver cache and any items in your local C:WindowsSystem32etcdrivershosts file.

Inspecting the DNS resolver cache
The /displaydns switch is especially helpful for troubleshooting name resolution issues!
Purging the DNS Resolver Cache
Sometimes the DNS resolver cache caches items you’d like to remove. You can clear out all items in the DNS resolver cache by running ipconfig /flushdns. This command is useful to remove any negative cache entries when troubleshooting.

Purging the DNS Resolver Cache
Initiating a Dynamic DNS Registration with an IPconfig Command
Perhaps you need to manually initiate a dynamic DNS registration and refresh DHCP releases. In that case, use ipconfig /registerdns. This ipconfig command is great for troubleshooting DNS name registration issues without rebooting the computer.
Be sure you use the /registerdnsswitch in an elevated console.

Initiating a Dynamic DNS Registration
Releasing and Renewing DHCP-Assigned IPs
One of the most common ipconfig commands is those that release and renew a dynamically-assigned (DHCP) IP address. To release a DHCP address, you can either do so by running ipconfig /release which will release all NICs bound by TCP/IP.

Releasing a DHCP address for the Ethernet NIC
Do you have more than one NIC with a similar name? No problem. Use a wildcard (*).

Releasing a DHCP address for all NICs that start with Eth
You can use wildcards for the NIC name on any ipconfig command that allows you to input a NIC’s name. You can also use a ? to represent a single character to match too.
Once the IP is released, you need to pull another one from your DHCP server. To do so, run ipconfig /renew to renew all NICs or specify a specific NIC again.

Getting a new DHCP lease on all NICs
Quick tip: You can release and renew dynamically-assigned IP addresses on the same line using double ampersands like ipconfig /release && ipconfig /renew.
If you’d like to limit releasing and renewing only IPv6 NICs, you can also use the /release6 and /renew6 parameters.
Note that ipconfig commands like /showclassid, /setclassid and /allcompartments parameters. These parameters are not covered in this Nugget because they are considered legacy and you will rarely (if ever) need them.
Из данной статьи вы узнаете, как очистить DNS кэш, который является собранием адресов недавно посещенных сайтов. Очистка DNS кэша зачастую исправляет проблему с ошибкой «Страница не найдена» и прочие неисправности с DNS.
- Откройте меню Пуск . Для этого нажмите на логотип Windows в нижнем левом углу экрана или нажмите клавишу .
- Введите в меню «Пуск» фразу командная строка. После этого на компьютере будет запущен поиск программы «Командная строка».
- Нажмите на Командная строка . Это будет первая иконка вверху меню «Пуск». Нажмите на эту иконку, чтобы открыть программу «Командная строка».
- Введите ipconfig /flushdns и нажмите , чтобы очистить DNS кэш компьютера.
- Перезагрузите браузер. Теперь у вас получится подключиться к ранее заблокированной странице.
Введите в Terminal следующий код:
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder;say DNS cache has been flushed
и нажмите . После этого будет выполнена команда очистки DNS.
Советы
- На Windows можно на некоторое время отключить DNS кэширование. Для этого откройте Командную строку и введите stop dnscache. Это приведет к остановке DNS кэширования до следующей перезагрузки компьютера.
- Если вы захотите очистить DNS кэш мобильного устройства, лучше всего это сделать путем жесткого перезапуска, что включает в себя выключение и включение телефона или планшета кнопкой питания.
Предупреждения
The ipconfig command is used in Windows to display information about a computer’s network interfaces.
To execute the ipconfig command open the Windows Command Prompt (cmd) and type ipconfig. The command will display information about each of the network interfaces (NICs) on the computer. Here is the output for a single network interface:
ipconfig
Windows Configuration
Wireless adapter WiFi
Connectionspecific Suffix xyzstprovidernet
IPv6 Address f064d977f
Temporary IPv6 Address bfae6
Temporary IPv6 Address f988d
Linklocal IPv6 Address fe80f064a1af
IPv4 Address
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway fe80eff
The default output includes information on the interface’s IP addresses, subnet mask, and default gateway (router). To obtain additional information such as DHCP and DNS settings use the /all option. It will also display information about the physical interface such as the MAC address and device description:
ipconfig all
Windows Configuration
Wireless adapter WiFi
Connectionspecific Suffix xysstprovidernet
Description Dual Band
Physical Address
Enabled Yes
Autoconfiguration Enabled Yes
IPv6 Address f064f
Temporary IPv6 Address f520fae6
Temporary IPv6 Address ab2bd
Linklocal IPv6 Address fe80a1af
IPv4 Address Preferred
Subnet Mask
Lease Obtained Friday April
Lease Expires Sunday April
Default Gateway
Server
DHCPv6
DHCPv6 Client
Servers
NetBIOS over Tcpip Enabled
Common Ipconfig Options
If your network adapter is configured to obtain an IP address automatically using DHCP you can reset it by using the /release and /renew parameters for ipconfig.
ipconfig release
ipconfig renew
This will reset the IP address on all network interfaces on the computer. To reset the IP address of just one interface, provide its name as an argument. If the interface name contains spaces be sure to enclose it in quotes.
ipconfig release “Wireless LAN adapter Wi-Fi”
Windows Configuration
The operation failed no adapter is the state permissible
operation
To obtain a true list of the network interface names use the wmic command:
wmic nic NetConnectionID
NetConnectionID
Ethernet
WiFi
Bluetooth Network Connection
Note that the interface is actually called “Wi-Fi”. That is the name you will need to use in ipconfig to release or renew the DHCP address for the interface.
Using Ipconfig to Display Your DNS Cache
In order to increase speed and efficiency computers often cache DNS information, at least for a short time period. You can use the /displaydns option for ipconfig to display your current DNS cache.
ipconfig displaydns
Windows Configuration
forcesafesearchgooglecom
Record Name forcesafesearchgooglecom
Record Type
Time To Live
Data Length
Section Answer
Host Record
To delete all of your DNS cache entries (flush) you can use ipconfig’s /flushdns option.
ipconfig flushdns
Windows Configuration
Successfully flushed the Resolver Cache
Setting a Network Interface’s IP Address
While ipconfig lets you display information, it cannot be used to change an interface’s IP address. For that you can use the netsh command, however, the command is being deprecated by Microsoft, so you are better of using PowerShell.
First open PowerShell and type Get-NetIPConfiguration. Below is an example of the output for a single interface. Note the interfaces InterfaceIndex.
netipconfiguration
InterfaceAlias WiFi
InterfaceIndex
InterfaceDescription Dual Band
NetProfileName wifissid
IPv6Address a1af
IPv4Address
IPv6DefaultGateway fe80d58e
IPv4DefaultGateway
DNSServer
Next set the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway for the interface using the New-NetIPAddress cmdlet:
NewNetIPAddress InterfaceIndex IPAddress PrefixLength DefaultGateway
Here is a breakdown of the parameters used:
-InterfaceIndex: The index of the interface you want to update
-IPAddress: The IP address you want to assign to the interface
-PrefexLength: The number of bits used by the subnet mask
-DefaultGateway: The IP address of the computer’s default gateway (router)
Next you can use the Set-DnsClientServerAddress cmdlet to specify the DNS servers for the interface to use:
-ServerAddresses: A list of the DNS servers to assign to the interface